Google used to make a slight number of updates per year, but now it brings thousands of updates per year. No, that's shocking! Search Engine Optimization is a detailed and progressive strategy, and updates should not have a major impact on your website rankings as long as you focus on EAT (expertise, authoritativeness, and trustworthiness) and best practices.
However, as a marketer, webmaster, or business owner, it is essential to monitor updates and review your performance in order to fine-tune your strategy and capitalize on available opportunities.
So, if you want to read about Google's significant algorithm updates, you've come to the right place. This article is a collection of all major Google Algorithm updates. However, first, grasp the concept of the Google Algorithm outlined below.
What exactly is the Google Algorithm?
The Google Algorithm is a complex system that retrieves data from its search index and instantly returns the best possible results for a query. And updates are designed to improve the end-user experience when visiting a specific website. This can have an impact on the website in both positive and negative ways.
Let's get started with the list of 21 major Google Algorithm updates.
The following are the most significant Google algorithm updates.
1. Panda – 24 February 2011
Panda is Google's first significant algorithm update, which was published on Feb 24, 2011. The update's main goal was to concentrate on the content quality score to website pages and de-scale the site with low-quality, spammy, or thin content. Panda used to give web pages a 'quality score.' This score is used by websites as a ranking factor.
Panda began as a filter rather than a component of Google's ranking algorithm, but in January 2016, it was officially upgraded to a core algorithm.
Panda's versions have also been updated, including:
Panda 2.0 was released on April 11, 2011, and included additional signals such as sites that Google users had blocked.
- Panda Update 2.1 was released on May 9, 2011.
- Panda Update 2.2 was released on June 21, 2011.
- Another Panda update 2.3 will be released on July 23, 2011.
- Panda Update 2.4 was released on August 12, 2011.
- Panda 2.5 was released on September 28, 2011.
- And the most recent Panda update 3.0 was on October 19, 2011.
Suggestion:
Content such as duplicate content, plagiarism, user-generated spam, poor user experience, thin content, and keyword stuffing would all be penalized under the Panda update.
To avoid Google penalties, use the site crawler to check keyword density, thin content, and duplicate content. You can use Website Auditor, a plagiarism checker tool.
2. Penguin – April 24, 2012
The penguin algorithm update is the next major update following Panda.
The penguin algorithm update is the next major update following Panda. The Penguin update was released on April 24, 2012. The Penguin update's main objective was to de-rank sites with links that appeared to be manipulative. It detects unnatural link profiles that are spamming search results by employing manipulative link strategies.
Penguin was incorporated into Google's core ranking algorithm in 2016, and it now operates in real-time.
The algorithm also ensures that penalties are now issued more quickly and that recovery takes less time.
Suggestion:
Spammy or irrelevant links, over-optimized anchor text, Paid links, and links from sites created solely for SEO link building are all unacceptable.
Backlink checker tool SEO SpyGlass should be used on a regular basis to audit your site. You can also check for the possibility of a penalty. Let me state unequivocally that Google will not penalize your site for having 1-2 spammy links, but a sudden influx of irrelevant backlinks can be problematic. Furthermore, you can request that spammy links be removed from the site.
3. Hummingbird – August 22nd, 2013
Hummingbird is another Google algorithm update that was released on August 22, 2013. The main goal of the update was to improve the interpretation of search queries as well as provide results that meet the searcher's intent. Hummingbird is unique in that it would rank a page for a request even if it does not contain the words exactly entered by the searcher.
Hummingbird also optimizes the use of synonyms. As a result, instead of displaying exact keyword matches, Google shows the most theme-related results in the SERPs which may or may not contain the query's keyword in their content.
Google stated that the Hummingbird update impacted approximately 90% of global searches.
Suggestion:
Low-quality content, exact-match keyword targeting, and Keyword stuffing are all heavily emphasized. To enhance your site's ranking, you must incorporate SEO keywords into your subject matter. Use synonyms and co-occurring terms sparingly. All of the Hummingbird-friendly search terms are included in SEO PowerSuite's Rank Tracker keyword research module.
4. Pigeon – July 24, 2014
Pigeon Google Algorithm update was released on July 24, 2014, in the United States. Another update was released on December 22, 2014, in the United Kingdom, Canada, and Australia. The update emphasized the importance of On-page and Off-page SEO quality.
According to Google, Pigeon strengthened ties between both the local and core algorithms, implying that the same Search engine factors are now being used to rank local and non-local Google results. Pigeon update ranks the results based on two key factors: location and distance.
Suggestion:
Majorly focus on poor on-and-off-page SEO, lack of citation in local directories, inconsistent NAP, poorly optimized pages, and irrelevant Google My Business Page setup.
Make an investment in both on-page and off-page SEO. To perform an on-page analysis, use the Website Auditor tool. Optimize your pages appropriately. Furthermore, you can examine a list of off-page SEO in relevant business directories. Your site will rank higher in Google's SERPs if you take this approach.
5. Google mobile-friendly update – April 21st, 2015
On April 21, 2015, the mobile-friendly update was released. The update (dubbed Mobilegeddon) was released to ensure that smartphone users could easily access the website. Mobile-friendly websites will rank at the top of mobile search results, while pages that are not optimized for mobile will be penalized and will be filtered out of SERPs or will rank lower.
Furthermore, this update has no effect on desktop searches. Since 2015, all digital marketing firms have been creating mobile-friendly websites.
Suggestion:
Better viewpoint configuration, poor mobile usability, Illegible content, the absence of a mobile version of a website, and a non-mobile-friendly website.
6. RankBrain – October 26th, 2015
On October 26, 2015, Google released yet another major algorithm update. Google's Hummingbird algorithm includes Rank Brain. Essentially, it is a machine learning system that assists Google in better understanding the meaning behind queries and determining how best to respond to those queries.
RankBrain can also summarise a page's content and assess the relevance of search results. RankBrain is the 3rd biggest ranking factor, as per Google.
The RankBrain algorithm identifies query-specific ranking keywords that are relevant features for website pages ranking for a given query.
Suggestion:
Poor user experience, low-quality or non-existent content, and a lack of query-specific relevance features. To provide a better user experience, you must conduct a competitor analysis. Keep track of your users' activities with Google Analytics, such as session duration, bounce rate, and so on.
7. Possum Update – September 1st, 2016
The update was released on September 1, 2016. This algorithm is well-known for introducing a slew of changes to Google's local ranking filter. The closer you are to a business's address, the more likely it will appear in local search results.
Following the Possum, Google displayed more varied results based on the searcher's physical location. Furthermore, Possum boosted businesses located outside of the physical city limits.
Suggestion:In your targeted area, take a glance for competitors who share a physical location with a similar industry, and look for competing companies whose business is closer to the searcher's location.
You can broaden your relevant keywords and track rank by location. It is critical that you track your positions for each variation separately. To look for variations, launch SEO PowerSuite's Rank Tracker and create and open a project. Now navigate to the keyword analysis module and select suggested keywords.
8. Fred Update– March 8, 2017
Fred In 2017, Google released an algorithm update. The update targeted websites that did not follow Google's webmaster guidelines. As a result, the majority of the affected sites are blogs with low-quality posts. These posts were created primarily to generate ad revenue or affiliate revenue.
Marketers or webmasters who create these types of sites to generate revenue will be penalized as a result of this update.
Suggestion:Ad-centered, low-quality, content that is thin and heavily reliant on affiliates.
Peruse the Google Search Quality Guidelines and keep an eye out for thin content. Even though you display ads, ensure the pages are of great quality, relevant to the offer, and have plenty of information.
You can't fool Google with a page full of affiliate links. If you do this, your website will be penalized soon.
9. March 2018 – Broad Core Algorithm Update
Google launched the Broad Core Algorithm Update on Twitter on March 2. This update concentrated on getting a greater understanding of the user's search queries and website. The primary goal is to improve Google's accuracy in corresponding search queries in order to have a better user experience and satisfaction. As a result, pages that were not previously rewarded will now rank higher.
Suggestion:Sites are being targeted for ranking signals, quality assurance, and the incorporation of new features to improve user experience.
All you have to do is concentrate on creating high-quality content, building high-quality backlinks, and sending out social signals. Content should be relevant to the keyword and phrase that your audience is looking for.
10. BERT Update – October 25th, 2019
BERT is the most significant algorithm update, which was released on October 25, 2019. To better understand search engine queries, Google used the BERT model. According to Google, this change had an impact on both search rankings and featured snippets. BERT Update is all about a deep learning algorithm for natural language processing.
It assists the machine in learning what a word means in a sentence with all of the nuances of the context.
Suggestion:Understanding the context of the sentence, improving search query comprehension, and avoiding the use of sloppy content
To keep safe, you must continue to optimize your posts, which may include images or videos, that you publish on your website.
This update was released last year, January 2020. This algorithm change had a significant impact on all search terms or results on a global scale. According to Google, core updates are "significant broad changes to our search algorithms in order to present pertinent and authoritative content to searchers."
Suggestion.
Concentrate on producing high-quality content; excellent content is rewarded, and ultra-spammy content is de-indexed.
Don't overcrowd your site with affiliate links; you can't fool Google in any way. Produce high-quality content and avoid adding low-quality links to the site.
12. Google Core Update — May 4, 2020
The second update of 2020 was once again announced on the day the update was released.
Another core update closely linked to the EAT and Medic signals was the Google May 2020 Core Update. It restructured ranking factors, giving more weight to brand factors, content, and user data.
This intended that while larger businesses benefited from the update, sites in the YMYL categories with potentially untrustworthy financial and health information suffered.
13. Google Core Update — December 3, 2020
Google delivered the third major update of 2020 as an early Christmas present. It began on December 3rd and took about a week to complete.
The December 2020 Core Update did not affect many websites, but those that were affected experienced major changes. Because it was so close to the release of passage indexing, it is thought to have focused on content interpretation and search intent.
The update, however, primarily impacted reference and news websites, where SERP (Search Engine Results Page) features became more prominent. However, many smaller retail websites experienced initial losses that were quickly reversed.
The most important Google algorithm updates are in 2021.
14. Passage Ranking Revision (February 2021)
Google can now use AI technology to index not just web pages, but also individual passages (passages, sentences) from those web pages, thanks to the passage ranking update. As a result, particular passages may appear as the featured snippet. Rather than making the user comb through relevant website pages to find out the answer, the goal is to quickly respond to very specific queries.
Suggestion:The point here is not to optimize your articles for passage ranking, but rather to:
- Long-tail keywords should be targeted.
- Provide detailed, high-quality content on the subject.
- Structure your webpage content properly and make Googlebot's indexing relatively easy.
15. A revision to the "About this Result" section - February 2021
Google's "About this result" feature, which was introduced in February 2021, adds context to individual search results, allowing users to determine which results will be most useful to them.
- The "About this result" box contains the following information:
- When Google first indexed the page's website.
- Check to see if your connection to the site is safe and protected.
- Which terms from your search appear on the page?
- Whether or not other websites containing those keywords link to the page.
- The language used on this page.
- Whether it appears relevant for this search in a variety of regions.
If you have a reference on Wikipedia, it will pull a short outline from there not meta tags.
Users can determine whether a site is trustable or not by learning about it before entering the results. This would especially help users find authoritative and trustworthy but unpopular sites on the internet. However, the feature is still in beta.
The "About this result" box has no bearing on your ranking; it's simply a list of page facts, some of which may be ranking factors. This includes the following:
- Ensure that your website uses HTTPS.
- Obtaining high-quality backlinks.
- Appropriately matching the keyword's purpose.
16. Updated Indexing to be entirely mobile-first (March 2021)
With the increase of mobile traffic in the 2010s, Google began emphasizing mobile-friendliness as a ranking factor. A year afterward, Google announced mobile-first indexing, which refers to when Google crawls—and thus ranks—your webpages based on the mobile version of that content.
Mobile-first indexing had become the de facto standard for all new sites in July 2019. And it will be the default for all websites, old and new, as of June 2021.
To make your website more mobile-friendly, follow these steps:
- Ensure you have a responsive website.
- Lazy loading and image compression should be used.
- On your smartphone, always manually check popups and form functionality.
Mobile-friendliness functions on a page-by-page basis, but site-wide mobile performance indicators can be found in Search Console's mobile usability report and Google's Mobile-Friendly Test tool.
Lazy loading is an excellent Search engine technique. It means the practice of delaying the loading of images on a site when they are required. The images are really not loaded until the user sees them on the screen. The image appears when the user scrolls to the section of the page that contains the image.
17. Product reviews have been updated (April 2021)
The goal of this major Google algorithm update was to encourage product reviews that provided in-depth research, original content insightful analysis, and rather than simply summarizing a range of products.
So, in order to develop high-quality product review content, it is recommended that you:
- Demonstrate extensive knowledge of the products.
- Share content that is different from what the manufacturer offers.
- Focus on providing quantitative performance measurements.
- Make a comparison to earlier models and other products.
- Assist customers in making sound purchasing decisions.
18. MUM Status Report (May 2021) - Multitask Unified Model
Google has made progress with AI in its algorithms, the most recent of which was the May 2021 MUM update.
The MUM is a natural language model that is far more powerful than the BERT of October 2019. (bidirectional encoder representations from transformers).MUM is intended to "assist you when there isn't a simple answer." MUM's aim is to propose detailed answers to complex questions by combining contextual information from various sources.
Multitask Unified Model (MUM) is being trained in 75 languages so that it can recognize relevant answers in languages other than the one in which the query was written.
This does not imply that you should begin writing posts in which you answer complicated questions. Just make sure to perform keyword research and continue to post long-form content that focuses on long-tail and question keywords.
19. Update on Link Spam (June 2021)
Google's spam algorithm update for June 2021 was deployed on the website page and image results.
It was divided into two phases, each of which Google promised would begin and end on the same day—but it took two weeks longer than planned. There weren't many specifics in this update, but it's always a good idea to double-check and ensure your website is spam-free.
You should always be careful of these malicious actors if your website allows for user interaction through forums, comments, and so on.
So here are a few simple tips to help you protect your site from spammers:
- Update the SSL certificate on your website.
- To verify for security risks and manual activity reports, use Google Search Console.
- Perform regular clean-ups of suspicious spammy activities, such as multiple requests from the same IP address.
- Noindex can be used to prevent Google from indexing low-trust pages, particularly those that show user-generated content. You could also mark the links as nofollow.
20. Page Experience Improvement (June 2021)
In addition to indexing mobile versions of sites, Google has launched a new set of metrics known as Core Web Vitals as part of the page experience update. These are newly prioritized factors for quantifying a user's experience with a website.
These are some examples:
- Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS): the degree to which the layout is stable (— in other words, elements do not jump around unexpectedly).
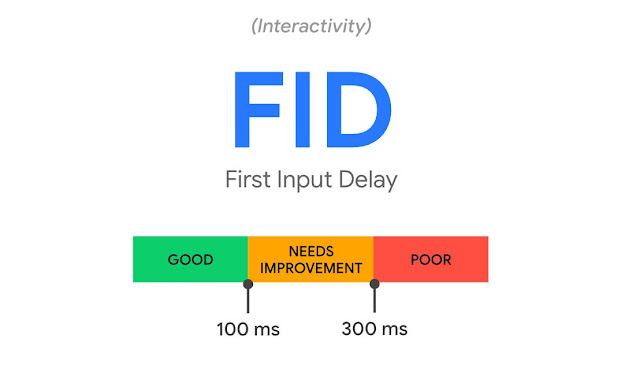
- First Input Delay (FID): the time it takes for a website page to respond to the user's first action on the page.
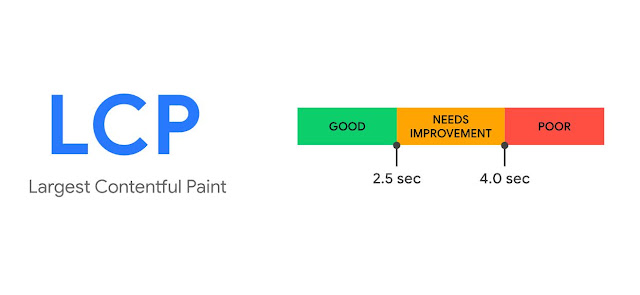
- Largest Contentful Paint (LCP): how quickly a page's main content loads.
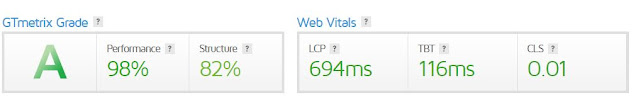
The actual data for such metrics can be found in Search Console's Page Speed Insights or the full Core Web Vitals report. All of these reports include suggestions for enhancing the page's responsiveness.
These metrics, once again, have been around for a long time. However, they now have a greater influence on your rankings. In essence, webmasters must increase their UX optimization efforts.
You can improve your Core Web Vitals by doing the following:
- Remove any interstitials or banners that obstruct content.
- Javascript execution should be reduced.
- Utilize lazy loading.
- Image optimization and compression
- Give images and embed proper dimensions.
- Enhance server response time.
21. Title Change on The Page (August 2021)
Google has been adjusting page titles in the SERP based on the query for more than a decade. However, beginning on August 16, users began to notice that Google was drastically changing their page titles, often in a negative way.
A week afterward, Google confirmed that it had announced a new system that will no longer adjust titles based on queries, but rather on how the page as a whole is represented.
[Recap] Google algorithm updates - till 2021
The following are the updates we discussed in this article:
1. Panda – 24 February 2011
2. Penguin – April 24, 2012
3. Hummingbird – August 22nd, 2013
4. Pigeon – July 24, 2014
5. Google mobile-friendly update – April 21st, 2015
6. RankBrain – October 26th, 2015
7. Possum Update – September 1st, 2016
8. Fred Update– March 8, 2017
9. March 2018 – Broad Core Algorithm Update
10. BERT Update – October 25th, 2019
11. Core Update for January 2020
12. Google Core Update — May 4, 2020
13. Google Core Update — December 3, 2020
14. Passage ranking revision (February 2021)
15. A revision to the "About this Result" section - February 2021
16. Product reviews have been updated (April 2021)
17. Product reviews have been updated (April 2021)
18 MUM status report (May 2021) - Multitask Unified Model
19. Update on link spam (June 2021)
20. Page experience improvement (June 2021)
21. Title change on the page (August 2021)
To End Up -
Finally, here is a comprehensive list of major Google algorithm updates from 2011 to 2020. I have only mentioned major updates that I believe are most important for every digital marketer, SEO, webmaster, or industry expert to be aware of.
I hope that this post was helpful in understanding the concept of significant Google Algorithm Updates.

![The Ultimate Guide to Google Core Web Vitals: Tips and Techniques [2023] The Ultimate Guide to Google Core Web Vitals: Tips and Techniques [2023]](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEiBZRfrxRpWvRbQUHKU6aq4hj95U63jiOFfxI2q0fQEhz_mTTRagC17P0APiPCOsHAfRS6q5qZSZCFMkuD7ZC4UqiljJMAunbLzcxdbYSy5nCcPGXTq3Dpa_gupJ6RNS_LX7yhXHvXi1ghiBx2VwC3hvmIXOQucSbwpTK--nlJhB2PllMoOPu8b7NZJ/w991/Google-Core-Web-Vitals.jpg)































![15 Travel Packing Tips For Holiday: Updated [2023] 15 Travel Packing Tips For Holiday: Updated [2023]](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEgJfOBYMtma5U34TjVvkOWNnaRwVA_ty2-tKck6tTU24-cAcOu4boybt3T_8BF66hAqzOriHVxJdRbzjLq9ZfhsMAUTQ80ja19GPktAAEnW0WPKQgsKJTXXJzIeKHYE40HeljCSC6UVTJA/s72-w640-c-h360/Travel-packing.jpg)
![The Best Antivirus Apps For Android - [2023] The Best Antivirus Apps For Android - [2023]](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEj3Yjm36h1U18dmYifXs9XZCUy6ch_XK0XOXf8hVW4zcVUDW0OiVXQZT0Sr77Yjep1CUOHP3OqlrMIzRJLYasizRmQUilnXjozbQ8D0iroUBbeFEUD2MwaJdGuE4RJaqrfVHFX-_OoIhOyPr_K10ky6goZUJtdqUWIOkCibIoNylnXXzR-AksQYPTQ0/s72-w640-c-h388/antivirus-android-2023.png)

