On May 28, 2020, Google unveiled Core Web Vitals - a set of metrics designed to enhance user experience and elevate website ranking. By evaluating speed, responsiveness, and visual stability, Core Web Vitals offer increased opportunities for improving website ranking.
In this post, we'll provide an in-depth look at Google Core Web Vitals and their impact on Google's ranking system. Additionally, we'll explore how these metrics can assist web developers and site owners in gaining insight into visitor behavior. Our goal is to make this information accessible and easy to understand for our readers.
To begin, let's dive into the fundamentals of Core Web Vitals.
An Overview of Google Core Web Vitals
Google employs Core Web Vitals, a group of metrics that evaluate user experience more accurately. These metrics are connected to page load time, page interactivity, and content visual stability during loading.
Google's mission is to provide the best user experience for its searchers by ensuring that all websites in its index meet a high standard. As per Google's official statement, the search engine prioritizes pages with the most useful information. Consequently, the Google Web Vitals have become a vital ranking signal. It is essential to assess the new Page Experience scores or signals.
These scores are calculated for each page on both desktop and mobile devices. Improved website performance could lead to increased visibility.This is an excellent time to review other essential aspects of your website, such as on-page optimization, content depth, and internal linking.
The Significance Google Core Web Vitals
Google's Core Web Vitals not only affect user experience but also influence page performance. Google aims to prioritize a page's experience as a critical factor in determining a website's ranking.
Therefore, your company's website's page experience score will most likely be based on these Core Web Vital metrics.
It's essential to note that while a high page experience score is vital, it's just one of several factors that contribute to search engine optimization (SEO) ranking. It won't automatically guarantee a top spot for your website.
Here are three compelling reasons why website owners must prioritize Core Web Vitals:
1- Enhance User Experience to Boost Revenue: Fast, user-friendly, and accessible from any device or location - these are the qualities visitors appreciate in a website. By prioritizing user experience, you can improve your website's appeal and increase revenue.
2- Core Web Vitals: A Crucial Ranking Factor: Core Web Vitals have emerged as a crucial ranking factor. Although relevance still holds more significance, we expect Core Web Vitals to gain more importance over time, affecting website ranking.
3- Good User Experience Equals Better SERP Ranking: A website that passes the Google Core Web Vitals test delivers a good user experience, resulting in fewer users returning to the SERP. Google has also introduced a "Good Page Experience" badge in search results. This is an indirect ranking factor that affects searcher behavior, leading to more clicks on pages with this badge, ultimately impacting Google's algorithms.
Core Web Vitals Metrics:
Let's get started by examining the Core Web Vitals - the key metrics that determine page experience.
To measure page experience, we'll delve into three crucial Web Vitals metrics that site owners need to focus on.
This post will also cover other non-Core Web Vitals metrics in detail later on.
Each metric provides a clear picture of the quality of a specific aspect of the page experience.
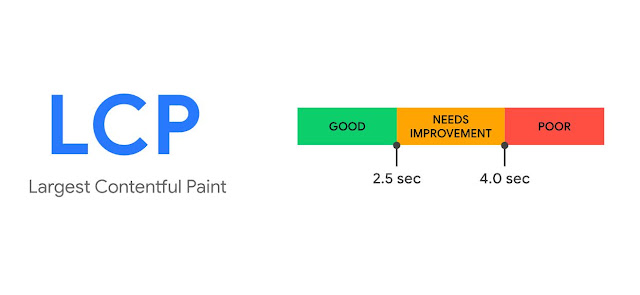
Largest Contentful Paint (LCP)
The Largest Contentful Paint (LCP) is a crucial metric that determines how quickly the largest element on your website loads. This element could be an image, text block, video, or animation, and may vary depending on the device used to access the website.
The LCP element is typically located at the top of the page, above the fold, and is the most important factor in determining perceived load speed and user experience. A faster loading time for LCP is always better for users.
To put it simply, LCP measures the time it takes for the largest element on your webpage to become visible. A slow LCP could lead to poor user experience, causing visitors to abandon your site.
Google recognizes the significance of LCP and has included it in the Google Core Web Vitals metrics. This means that LCP plays a significant role in determining how well your website ranks in terms of user experience. Therefore, it is crucial to focus on improving your LCP score to ensure a fast and seamless user experience.
Important Factors To Consider
When it comes to the Largest Contentful Paint (LCP) metric, there are a few important factors to keep in mind. The biggest text block or image element on a page is what's being measured, and it can change while the page is loading. The most recent candidate is used to calculate the LCP.
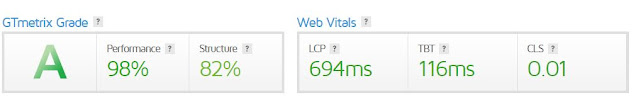
It's important to note that "SVG" elements are currently not considered for the LCP calculation, but this may change in the future. The LCP score has a standard set by Google, with a good score being 2.5 seconds or less. A score between 2.5 and 4 seconds needs improvement, while a score over 4 seconds is poor.
There are various factors that can cause a low LCP score, including slow server response times, render-blocking JavaScript and CSS, and large content resources. To improve your LCP score, make sure your images are compressed and in the next-generation format, with image sizes around 100 KB or less. Scaling and defining image sizes can also help.
Improving the LCP metric can be challenging due to the many variables that can influence it. Optimizing your critical rendering path, CSS, and images can help improve your LCP score. Remember, a good LCP score not only provides a great user experience but also improves your SEO performance.
Lastly, the LCP metric accounts for 25% of the total PageSpeed Insights score, so improving it can also improve your page speed grade. In summary, the LCP is one of the most important performance metrics you should focus on to provide a great user experience and improve your website's overall performance.
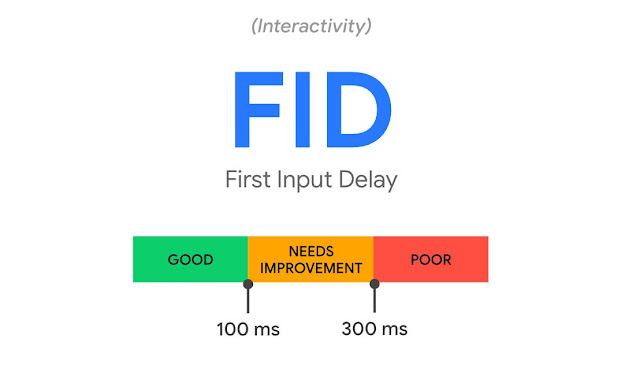
Understanding First Input Delay (FID) and Its Significance for Website Performance
First Input Delay (FID) is a crucial metric for website owners to measure as part of their Google Core Web Vitals. It evaluates how fast a web page can respond to a user's first interaction, such as clicking a button, tapping a link, or pressing a key.
FID is measured in milliseconds, and it is the time elapsed between the user's first interaction with the website and the browser's response to that action.
Imagine you land on a website and click a link or button, expecting the page to load quickly. Unfortunately, this isn't always the case. You may have to wait a few seconds for the browser to respond, which can be frustrating. This delay is typically due to the browser being busy with another request, usually related to JavaScript files processing.
To improve user experience and ensure that visitors do not abandon your website, it is important to keep FID scores low. This metric helps to measure how quickly a web page can respond to user input, and ultimately, it impacts your website's overall performance and search engine ranking.
Important Factors To Consider
First Input Delay (FID) is a crucial Google Core Web Vitals metric that measures how long it takes for a browser to respond to a user's first interaction with a webpage. Note that actions like scrolling or zooming are not considered in FID measurements.
Because FID is based on user interaction, it can only be measured in the field, making it different from other Core Web Vitals metrics that can be evaluated in a laboratory setting. Lighthouse and other tools rely on Total Blocking Time (TBT) as a proxy to measure interactivity and responsiveness in the absence of user interaction. However, a low TBT score typically correlates with a good FID score.
To achieve a good FID score, you need to focus on reducing JavaScript execution time, minimizing main thread work, and reducing the impact of third-party code. A high FID score indicates that the browser is not able to respond to user interaction quickly, which can lead to a poor user experience.
Improving FID performance can also have a positive impact on your page speed score. A good FID score is less than or equal to 100ms, while a score greater than 100ms and less than or equal to 300ms requires improvement. Scores over 300ms are considered poor.
For more information on improving FID scores, we recommend exploring the resources available on web.dev. Remember that improving FID scores is just one aspect of optimizing your website for search engine optimization.
Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS)
The Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS) is a crucial Google Core Web Vitals metric that measures the visual stability of a page and its impact on the user experience. Whenever the content on a page changes, even if you haven't clicked on anything, it can cause a layout shift. This metric is available in both field and lab data formats, and a lower CLS score indicates better visual stability.
Layout shifts can be frustrating for users and occur for various reasons, such as new images or ads loading above the fold, which pushes the content down, causing it to shift its position on the page. These shifts can make it difficult for users to interact with the page, resulting in a poor user experience.
The Cumulative Layout Shift is a vital metric that, along with the Largest Contentful Paint and First Input Delay, was added to the Page Experience ranking factor in June 2021. It accounts for 15% of the PageSpeed score, making it highly relevant to SEO performance.
Unlike other metrics, CLS is not measured in seconds; instead, it refers to elements that move between two frames and measures their movement in the viewport based on the size of the viewport. The layout shift score comprises two components: the "distance fraction" and the "impact fraction."
Improving the visual stability of a page can be achieved by optimizing images, videos, and ads, among other things. You can use the "layout instability" report in Google Search Console to identify and fix issues related to layout shifts. Improving your CLS score will result in a better user experience, improved SEO performance, and increased user engagement on your website.
To calculate the Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS) score, Google Core Web Vitals considers two components: the "impact fraction" and the "distance fraction." The impact fraction is the percentage of the viewport occupied by the unstable element in both frames, while the distance fraction is the maximum distance that the unstable element travels between the frames divided by the larger dimension of the viewport (width or height).
CLS measures the visual stability of a webpage, which is critical to user experience. Have you ever experienced content shifting when you try to click a button, or an ad loading and pushing other elements down? These are examples of layout shifts, which can be frustrating for users. CLS is one of the three Core Web Vitals metrics that assess the user experience of a webpage, along with Largest Contentful Paint and First Input Delay. In June 2021, these metrics were added to the Page Experience ranking factor, accounting for 15% of the PageSpeed score.
CLS can be measured using both field and lab data and is not measured in seconds. Instead, it refers to elements that move between two frames and calculates their movement in the viewport based on its size. Improving visual stability can result in a better CLS score and ultimately lead to better SEO performance.
Important Factors To Consider
Consider the following important factors when it comes to optimizing your page's user experience:
The Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS) is a metric that measures the visual stability of a page during its entire lifecycle, which means that the CLS score is measured even if the page remains open for days or weeks. However, keep in mind that CLS field data and lab data may differ since lab data is only collected for a short time.
Testing for unexpected layout shifts in test environments can be challenging, as some functionalities may be disabled or behave differently, such as disabled cookie notifications or live chat support, and unloaded personalized content.
To achieve a good CLS score, the score should be <=0.1. A score of >0.1 and <=0.25 needs improvement, while a score of >0.25 is poor.
Poor CLS scores are often due to images or ads with undefined dimensions, asynchronously loaded resources, and the addition of new DOM elements dynamically to a page above previously loaded content. This causes content that has already been loaded to be removed.
Improving your CLS score can be achieved by including size attributes for images and videos and avoiding inserting content above previously loaded content. You can also check out web.dev's article on optimizing CLS scores to learn more.
Other non-Core Web Vitals include Total Blocking Time (TBT), Speed Index (SI), and Time to Interactive (TTI).
Total Blocking Time (TBT)
Total Blocking Time (TBT) is a metric that measures the duration in milliseconds between the First Contentful Paint (FCP) and Time To Interactive (TTI) when the main thread becomes unresponsive to user input. A high TBT score can result in a poor user experience, and it is crucial to keep this metric low. The TBT score is rated as good if it is below 200ms, needs improvement if it falls between 200ms and 600ms, and poor if it exceeds 600ms.
The Speed Index (SI) measures how fast the contents of a page are visible during page load. This metric analyzes the visual progression of the page frame by frame, with frames being captured every 100ms. A low SI score can lead to a poor user experience, and it is essential to keep this metric as low as possible. A good SI score is below 3.4s, needs improvement if it falls between 3.4s and 5.8s, and poor if it exceeds 5.8s.
Optimizing your TTI Score
Improving your TTI score involves enhancing your page's load performance by minimizing the amount of time required to display the most important content and interactive elements. Here are some tips to improve TTI:
Minimize and defer the loading of non-critical resources.
Optimize the critical rendering path to ensure that the browser can quickly render the most important content and interactive elements.
Implement code splitting to reduce the amount of JavaScript that needs to be downloaded and parsed.
Use web workers and requestIdleCallback to offload resource-intensive tasks and ensure that the main thread remains responsive to user interactions.
To learn more about how to optimize TTI, you can refer to the web.dev's guide on improving page load performance.
What might be causing a low TTI score?
There are several factors that can contribute to a low TTI (Time to Interactive) score. Some of the most common ones are:
Large JavaScript and CSS files: When the browser has to download large JavaScript and CSS files, it can slow down the page load time and delay the TTI.
Render-blocking resources: When resources such as scripts, stylesheets, and fonts are render-blocking, the browser has to wait for them to load before rendering the page, which can delay the TTI.
Slow server response time: If the server takes a long time to respond to requests, it can delay the TTI.
Third-party scripts: Third-party scripts such as social media widgets, chatbots, and tracking codes can slow down the page load time and delay the TTI.
Heavy images and videos: Large image and video files can take a long time to load, which can slow down the page load time and delay the TTI.
To improve your TTI score, you can work on optimizing these factors, such as reducing the size of JavaScript and CSS files, eliminating render-blocking resources, improving server response time, minimizing the use of third-party scripts, and optimizing images and videos.
Does Core Web Vitals Affects SEO
Yes, Core Web Vitals do affect SEO. Core Web Vitals are a set of user-focused metrics that measure the speed, responsiveness, and visual stability of web pages. Google has announced that starting from May 2021, these metrics will be used as ranking signals in search results. This means that web pages that provide a better user experience, as measured by Core Web Vitals, are more likely to rank higher in search results.
Core Web Vitals consist of three metrics: Largest Contentful Paint (LCP), First Input Delay (FID), and Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS). These metrics measure the loading speed, interactivity, and visual stability of web pages, respectively.
While Core Web Vitals are not the only factors that Google considers when ranking web pages, they are an important part of the overall ranking algorithm. Websites that prioritize user experience and optimize for Core Web Vitals are more likely to rank higher in search results and attract more organic traffic.
The Impact of Web Vitals on Traffic Sites check
During a meeting, John Mueller, a Google SEO specialist, addressed the question of how to determine whether Core Web Vitals scores affect a site's ranking. He also shared insights into what to look for when a site's ranking is impacted and when it is not. One attendee discussed a 20% drop in organic search traffic after the Google update and asked if resolving Core Web Vitals issues would help regain traffic levels.
In response, John provided a detailed explanation. He explained that if the website had experienced a sudden drop in traffic on the exact update date, it was probably not related to Core Web Vitals. John confirmed that the updates happen automatically, and any changes to a website's Core Web Vitals will take effect gradually, without waiting for a major Google update.
It's crucial to understand the changes in Google's Page Experience since they impact rankings gradually, whether positively or negatively. Occasionally, changes in traffic numbers may be due to coincidence, and blaming it on Google's algorithm and Core Web Vitals won't be helpful.
In conclusion, resolving Core Web Vitals issues can help improve a site's ranking, but it is essential to keep in mind that other factors also influence search engine rankings.
Core Web Vitals check - Metrics Tools
If you want to check your website's Core Web Vitals, there are several metrics tools available to help you. These tools can provide valuable insights into your website's performance and help you identify areas for improvement.
Some popular Core Web Vitals metrics tools include Google's PageSpeed Insights, Lighthouse, and WebPageTest. These tools analyze your website's loading speed, interactivity, and visual stability, as measured by the three Core Web Vitals metrics: Largest Contentful Paint (LCP), First Input Delay (FID), and Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS).
Using these metrics tools, you can get a detailed report on your website's Core Web Vitals performance, including suggestions for how to improve each metric. By optimizing for Core Web Vitals, you can improve your website's user experience and potentially improve your search engine rankings.
It's important to keep in mind that Core Web Vitals are not the only factor that affects search engine rankings. However, they are an important part of the overall ranking algorithm, and optimizing for them can help your website perform better in search results.
Google now has six methods for measuring key web metrics.
- Search Console.
- PageSpeed Insights.
- Lighthouse.
- Chrome DevTools.
- Chrome UX Report.
- Web Vitals Extension
Conclusion
In conclusion, optimizing your website for page speed has always been important for SEO, with Pagespeed Insights and AMP being some of the tools used by Google to promote faster loading times. However, with the introduction of Google Core Web Vitals, page speed optimization has become even more integral to SEO.
It's important to keep in mind that optimizing for Core Web Vitals is just one aspect of SEO, and it may not yield immediate results on its own. But by making multiple improvements to your website's loading speed and user experience, you can ultimately improve your SEO performance.
In addition to optimizing for Core Web Vitals, there are other SEO best practices to consider, such as creating high-quality content, using relevant keywords, and building quality backlinks. By taking a comprehensive approach to SEO, you can improve your website's visibility and attract more traffic from search engines.
Read More:







![The Best Antivirus Apps For Android - [2023] The Best Antivirus Apps For Android - [2023]](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEj3Yjm36h1U18dmYifXs9XZCUy6ch_XK0XOXf8hVW4zcVUDW0OiVXQZT0Sr77Yjep1CUOHP3OqlrMIzRJLYasizRmQUilnXjozbQ8D0iroUBbeFEUD2MwaJdGuE4RJaqrfVHFX-_OoIhOyPr_K10ky6goZUJtdqUWIOkCibIoNylnXXzR-AksQYPTQ0/s72-w640-c-h388/antivirus-android-2023.png)
![15 Travel Packing Tips For Holiday: Updated [2023] 15 Travel Packing Tips For Holiday: Updated [2023]](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEgJfOBYMtma5U34TjVvkOWNnaRwVA_ty2-tKck6tTU24-cAcOu4boybt3T_8BF66hAqzOriHVxJdRbzjLq9ZfhsMAUTQ80ja19GPktAAEnW0WPKQgsKJTXXJzIeKHYE40HeljCSC6UVTJA/s72-w640-c-h360/Travel-packing.jpg)


0 Comments: